What is Data Governance
Data governance is like a set of rules and guidelines for how a company handles its data. It’s about making sure data is accurate, safe, and used properly. Think of it as a traffic system for your data, ensuring it flows smoothly and safely throughout your organization.
With data governance in place, everyone knows how to handle data, from collecting it to storing it and using it. This helps prevent mistakes, keeps data secure, and makes sure it’s available when needed. It’s all about treating data as a valuable asset and using it to make smart decisions.
Table of Contents
Who is Responsible for Data Governance
Making sure data governance rules are followed requires two types of roles in a company.
First, there are the leaders – officers, heads, and managers. They set the strategy, decide what the goals are, and are ultimately responsible for the results. Think of them as the captains of the ship. Some typical roles in this group include:
- Chief Data Officer: The top data person, responsible for the company’s overall data strategy.
- Data Security Officer: Makes sure data is kept safe and secure.
- Head of Data Governance: The person in charge of making sure the data governance rules are followed.
- Data Quality Manager: Ensures the data is accurate and useful.
Then, there are the experts – the people who actually do the work. They might perform tasks themselves or lead small teams. They’re like the crew of the ship, making sure everything runs smoothly. These roles include:
- Data Owner: The person in charge of a specific set of data.
- Product Owner: Represents the people who will use the data, making sure it meets their needs.
- Data Steward: Makes sure the data is accurate and well-organized.
- Data Custodian: The person who physically takes care of the data, storing it and keeping it safe.
- Data Quality Engineer: Uses technical skills to make sure the data is high quality.
So, it’s a team effort! The leaders set the direction, and the experts make it happen.
The following infographic describes all roles and their responsibilites.

Data Governance Committees
When different teams in a company need to agree on how to handle data, things can get tricky. Imagine trying to decide on one set of rules for both patient data in a hospital and information about company cars. It’s not always easy!
Disagreements are common, especially when rules needed for legal reasons in one area are forced on teams handling less critical data. To solve these problems and make sure everyone is on the same page, big companies often create data governance committees or boards.
These groups are like advisors. They talk about the company’s long-term plans for data, sometimes looking five years or even further into the future. The leaders – the officers and heads – are responsible for organizing these meetings, helping everyone discuss and agree, and then making sure the decisions are put into action.
Multi-Role Data Governance Positions
Most companies don’t need to have a separate person for every data governance role. They often combine responsibilities, especially if they’re not heavily reliant on data and don’t need a high-level executive dedicated to it.
In these cases, they might have a “Head of Data Governance” who takes on a broad range of tasks that would normally be split between a Chief Data Officer or Data Security Officer.
The same goes for the hands-on roles. It’s common to see the Data Owner, Data Steward, Data Custodian, and Data Quality Engineer combined into one position. Sometimes, these tasks are divided between a technical person focused on the nuts and bolts of data management and a more business-oriented person who makes decisions about data models, validation rules, and how to prioritize fixing data quality problems that impact the company’s operations.
In order to make a decision about what data governance roles are required, and which roles should be combined, the rest of this article lists all roles that are commonly seen in organizations, and describes their responsibilities.
Chief Data Officer (CDO)
The Chief Data Officer (CDO) is a senior executive responsible for leading an organization’s overall data strategy. They act as the champion for data-driven decision-making and ensure that data is treated as a valuable asset. The CDO’s role is crucial in establishing and maintaining a strong data governance framework, promoting data literacy, and driving innovation through data insights.
In essence, the CDO is the captain of the data ship, steering the organization towards a future where data fuels success. They work closely with other C-level executives to ensure data initiatives align with business objectives and contribute to the bottom line.
Responsibilities of a CDO
The responsibilities of a CDO are multifaceted and encompass both strategic and operational aspects of data management. Some key responsibilities include:
- Developing and Implementing Data Strategy: Creating a comprehensive data strategy that outlines how data will be collected, stored, managed, and used to achieve business goals.
- Establishing Data Governance: Setting up a robust data governance framework to ensure data quality, integrity, security, and compliance with regulations.
- Promoting Data Literacy: Educating employees across the organization about the importance of data and how to use it effectively.
- Driving Data Innovation: Identifying and implementing new technologies and approaches to leverage data for competitive advantage.
- Managing Data Teams: Leading and developing a team of data professionals, including data scientists, analysts, engineers, and stewards.
- Building Data Partnerships: Collaborating with external partners to acquire and share data that can create new business opportunities.
Accountability and Goals of a CDO
The CDO is ultimately accountable for the success of the organization’s data initiatives. They must ensure that data is being used ethically and responsibly to create value for the business and its stakeholders. Some key goals that a CDO typically strives to achieve include:
- Improving Data Quality: Ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and consistent across the organization.
- Enhancing Data Security: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse.
- Increasing Data Accessibility: Making data easily available to those who need it, while maintaining appropriate controls.
- Maximizing Data Value: Generating insights from data that lead to better decision-making, improved efficiency, and increased revenue.
- Fostering a Data-Driven Culture: Creating an environment where data is embraced and used to inform every aspect of the business.
By fulfilling these responsibilities and achieving these goals, the CDO plays a pivotal role in transforming an organization into a data-driven powerhouse.
Data Security Officer
The Data Security Officer is the guardian of an organization’s sensitive information. They are responsible for designing, implementing, and overseeing the company’s data security program. Their mission is to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage. This includes both internal and external threats, ensuring that data is handled in a secure and compliant manner.
In an increasingly digital world where cyber threats are constantly evolving, the Data Security Officer plays a crucial role in safeguarding the organization’s most valuable asset – its data. They act as a bridge between the technical aspects of data security and the business needs of the organization, ensuring that data protection measures are both effective and practical.
Responsibilities of a Data Security Officer
The Data Security Officer’s duties are wide-ranging and involve both proactive and reactive measures to protect data. Some of their key responsibilities include:
- Developing and Implementing Security Policies: Creating and enforcing policies, procedures, and standards for data security across the organization.
- Conducting Risk Assessments: Identifying and evaluating potential security risks and vulnerabilities, and developing mitigation strategies.
- Implementing Security Measures: Deploying and maintaining security technologies such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
- Managing Security Incidents: Responding to and investigating security breaches or incidents, and taking corrective action.
- Ensuring Compliance: Maintaining compliance with data privacy regulations and industry standards.
- Educating Employees: Providing training and awareness programs to educate employees about data security best practices.
Accountability and Goals of a Data Security Officer
The Data Security Officer is ultimately accountable for the overall security of the organization’s data. They are the first line of defense against cyber threats and must ensure that data protection measures are robust and up-to-date. Some of the key goals they aim to achieve include:
- Preventing Data Breaches: Minimizing the risk of unauthorized access, data leaks, or cyber attacks.
- Maintaining Data Integrity: Ensuring that data remains accurate, complete, and reliable.
- Ensuring Business Continuity: Protecting data availability so that the organization can continue operations in the event of a security incident.
- Building a Security-Conscious Culture: Fostering an environment where all employees understand the importance of data security and actively participate in protecting sensitive information.
Head of Data Governance
The Head of Data Governance is the orchestrator of an organization’s data governance program. They are responsible for establishing, implementing, and maintaining the framework that ensures data is managed effectively and efficiently across the enterprise. This role is particularly vital in organizations where a dedicated Chief Data Officer might not be present, making the Head of Data Governance the highest-ranking individual responsible for data-related matters.
In essence, the Head of Data Governance acts as the conductor of the data orchestra, ensuring that all data-related activities are harmonized and aligned with business objectives. They work closely with various stakeholders across the organization to establish data policies, standards, and procedures that promote data quality, integrity, and accessibility.
Responsibilities of a Head of Data Governance
The Head of Data Governance has a diverse set of responsibilities that span both strategic and tactical aspects of data management. Some key responsibilities include:
- Developing and Implementing Data Governance Framework: Creating and maintaining a comprehensive data governance framework that defines roles, responsibilities, policies, and procedures for data management.
- Establishing Data Standards: Defining and enforcing data standards, including data definitions, formats, and quality metrics.
- Managing Data Governance Committees: Leading and facilitating data governance committees or councils, ensuring that data-related issues are addressed and resolved effectively.
- Promoting Data Literacy: Educating employees about data governance principles and best practices.
- Monitoring and Measuring Data Governance: Tracking and reporting on the effectiveness of the data governance program, and identifying areas for improvement.
- Collaborating with Stakeholders: Working closely with data owners, stewards, custodians, and other stakeholders to ensure data governance policies are adhered to.
Accountability and Goals of a Head of Data Governance
The Head of Data Governance is accountable for the overall success of the data governance program. They must ensure that data is managed in a way that supports business goals and minimizes risks. Some of the key goals they aim to achieve include:
- Improving Data Quality: Establishing and maintaining high standards of data quality across the organization.
- Enhancing Data Accessibility: Making data readily available to those who need it, while ensuring appropriate access controls.
- Reducing Data Redundancy: Eliminating duplicate or unnecessary data to improve efficiency and reduce storage costs.
- Ensuring Data Compliance: Adhering to data privacy regulations and industry standards.
- Creating a Data-Driven Culture: Promoting the use of data to inform decision-making at all levels of the organization.
Data Quality Manager
The Data Quality Manager is the champion of data accuracy and reliability within an organization. They are responsible for establishing and overseeing the processes and systems that ensure data is fit for its intended purpose. This involves defining data quality standards, implementing data quality controls, and monitoring data quality metrics to identify and resolve any issues.
In essence, the Data Quality Manager acts as the quality inspector of the organization’s data, ensuring that it meets the highest standards of accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness. They work closely with data owners, stewards, and IT teams to embed data quality practices into every stage of the data lifecycle, from collection to reporting.
Responsibilities of a Data Quality Manager
The Data Quality Manager has a critical role in maintaining the trustworthiness of an organization’s data assets. Some of their key responsibilities include:
- Defining Data Quality Standards: Establishing clear and measurable data quality standards that align with business requirements and regulatory compliance.
- Implementing Data Quality Controls: Designing and implementing data quality checks, validation rules, and cleansing processes to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
- Monitoring Data Quality Metrics: Tracking and reporting on key data quality metrics to identify trends, issues, and areas for improvement.
- Resolving Data Quality Issues: Investigate and resolve data quality problems in a timely and effective manner, working with relevant stakeholders.
- Promoting Data Quality Awareness: Educating employees about the importance of data quality and their role in maintaining it.
- Selecting and Implementing Data Quality Tools: Evaluating and deploying data quality tools and technologies to support data quality initiatives.
Data Owner
The Data Owner is the business leader accountable for the value and use of specific data assets within an organization. They have the ultimate authority and responsibility for making decisions about how data is collected, stored, used, and shared. This role is critical in ensuring that data is aligned with business objectives and used ethically and responsibly.
In essence, the Data Owner acts as the steward of their assigned data domain, ensuring its quality, integrity, and security. They collaborate closely with data stewards, custodians, and other stakeholders to implement data governance policies and ensure compliance with regulations.
Responsibilities of a Data Owner
The Data Owner’s responsibilities encompass a broad range of activities related to data management and governance. Some key responsibilities include:
- Defining Data Requirements: Clearly articulating the business needs and requirements for data within their domain.
- Classifying Data: Assigning appropriate classifications and sensitivity levels to data based on its value and potential impact.
- Approving Data Access: Granting or denying access requests to data, ensuring that only authorized individuals have access.
- Ensuring Data Quality: Working with data stewards to monitor and maintain data quality within their domain.
- Enforcing Data Policies: Ensuring compliance with data governance policies and procedures within their area of responsibility.
- Collaborating with Stakeholders: Communicating effectively with other data governance roles and stakeholders to ensure alignment and cooperation.
- Making Data-Driven Decisions: Utilizing data insights to inform business decisions and strategies.
The Data Owner plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between business needs and data management practices. By effectively managing their assigned data assets, they contribute to the overall success of the organization’s data governance program and enable data-driven decision-making.
Product Owner
The Product Owner is the voice of the customer in the realm of data. They represent the needs and priorities of the end-users who rely on data to perform their jobs or achieve their goals. In the context of data governance, the Product Owner ensures that data initiatives and projects are aligned with business objectives and deliver value to the organization.
In essence, the Product Owner acts as a bridge between the business and the data teams, translating business requirements into actionable data projects. They collaborate closely with data stewards, architects, and engineers to ensure that data solutions meet the needs of the users and contribute to the overall success of the organization.
Responsibilities of a Product Owner
The Product Owner’s responsibilities revolve around understanding user needs, prioritizing data initiatives, and ensuring successful delivery of data solutions. Some key responsibilities include:
- Gathering and Prioritizing Requirements: Collecting and analyzing user needs and translating them into clear and concise data requirements. Prioritizing these requirements based on business value and strategic alignment.
- Managing the Product Backlog: Maintaining a prioritized list of data projects and features, ensuring that the backlog is transparent and accessible to stakeholders.
- Collaborating with Data Teams: Working closely with data architects, engineers, and analysts to design, develop, and implement data solutions.
- Communicating with Stakeholders: Keeping stakeholders informed about project progress, risks, and changes, and managing their expectations.
- Ensuring User Acceptance: Conducting user acceptance testing to ensure that data solutions meet the needs and expectations of the end-users.
- Monitoring and Evaluating: Tracking the performance and impact of data solutions and making adjustments as needed.
The Product Owner plays a pivotal role in ensuring that data projects are not only technically sound but also deliver tangible business value. By effectively advocating for the needs of the end-users and prioritizing data initiatives strategically, they contribute to the overall success of the organization’s data governance program and its ability to leverage data for competitive advantage.
Data Steward
The Data Steward is the guardian of data quality and meaning within a specific domain or business area. They are responsible for ensuring that data is accurate, complete, consistent, and aligned with business rules and definitions. This involves working closely with data owners, custodians, and users to understand data requirements, define data standards, and implement data quality controls.
In essence, the Data Steward acts as the subject matter expert for their assigned data domain, ensuring that data is fit for its intended purpose. They bridge the gap between business users and IT professionals, ensuring that data is understood and used effectively across the organization.
Responsibilities of a Data Steward
The Data Steward’s responsibilities encompass a range of activities focused on maintaining the quality and integrity of data. Some key responsibilities include:
- Defining Data Standards: Collaborating with data owners and users to define clear and consistent data definitions, business glossaries, and metadata.
- Implementing Data Quality Controls: Designing and implementing data quality checks, validation rules, and cleansing processes to ensure data accuracy and completeness.
- Monitoring Data Quality: Regularly reviewing and analyzing data quality metrics to identify and resolve any issues or inconsistencies.
- Resolving Data Issues: Investigating and resolving data quality problems, working with data owners, custodians, and IT teams to implement corrective actions.
- Communicating Data Definitions: Ensuring that data definitions and business rules are clearly communicated and understood by all data users.
- Educating Data Users: Providing training and guidance to data users on data quality best practices and data governance policies.
- Collaborating with Stakeholders: Working closely with data owners, custodians, and IT teams to ensure data quality and governance goals are met.
The Data Steward plays a vital role in ensuring the trustworthiness and usability of data. By actively managing data quality and promoting data literacy, they contribute to the overall success of the organization’s data governance program and its ability to make informed, data-driven decisions.
Data Custodian
The Data Custodian is the technical guardian of an organization’s data. They are responsible for the day-to-day management and protection of data assets, ensuring their availability, integrity, and confidentiality. This involves implementing and maintaining security measures, managing data storage and backup systems, and controlling access to data based on established policies.
In essence, the Data Custodian acts as the caretaker of the organization’s data, ensuring it is stored securely, backed up regularly, and accessible only to authorized individuals. They work closely with data owners, stewards, and IT teams to implement data governance policies and protect data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage.
Responsibilities of a Data Custodian
The Data Custodian’s responsibilities are primarily technical and operational, focused on the safekeeping and management of data. Some key responsibilities include:
- Implementing Security Measures: Deploying and maintaining security technologies such as encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems to protect data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Managing Data Storage: Overseeing the storage of data, ensuring it is organized, accessible, and compliant with data retention policies.
- Performing Data Backups: Implementing and managing regular data backup and recovery processes to protect against data loss.
- Controlling Data Access: Granting and revoking access to data based on established policies and user roles, ensuring that only authorized individuals can view or modify data.
- Monitoring Data Usage: Tracking and analyzing data access and usage patterns to identify potential security risks or anomalies.
- Collaborating with IT Teams: Working closely with IT teams to ensure that data storage and security systems are up-to-date and functioning properly.
- Responding to Data Requests: Fulfilling data access requests from authorized individuals in a timely and compliant manner.
The Data Custodian plays a vital role in protecting the organization’s data assets and ensuring their availability for business operations. By effectively managing data storage, security, and access controls, they contribute to the overall success of the data governance program and help maintain the trust and confidence of stakeholders in the organization’s data management practices.
Data Quality Engineer
The Data Quality Engineer is the technical expert responsible for ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of an organization’s data. They design, develop, and implement data quality solutions that identify and resolve data issues, ensuring that data is fit for its intended purpose. This involves using a variety of tools and techniques to profile, cleanse, and validate data, as well as monitoring data quality metrics and reporting on findings.
In essence, the Data Quality Engineer acts as the data detective, investigating and resolving data anomalies and inconsistencies. They work closely with data stewards, custodians, and IT teams to implement data quality rules and processes, ensuring that data is reliable and trustworthy.
Responsibilities of a Data Quality Engineer
The Data Quality Engineer’s responsibilities are primarily technical, focused on building and maintaining data quality solutions. Some key responsibilities include:
- Data Profiling: Analyzing data to understand its structure, content, and quality characteristics, identifying potential issues and inconsistencies.
- Data Cleansing: Designing and implementing data cleansing processes to correct errors, standardize formats, and remove duplicates or inconsistencies.
- Data Validation: Developing and implementing data validation rules and checks to ensure that data adheres to predefined standards and business rules.
- Data Monitoring: Setting up and maintaining data quality monitoring systems to track key metrics and identify potential data quality issues.
- Data Reporting: Generating regular reports on data quality metrics and findings, communicating results to stakeholders.
- Root Cause Analysis: Investigating the root causes of data quality issues and recommending corrective actions.
- Tool Selection and Implementation: Evaluating and deploying data quality tools and technologies to support data quality initiatives.
The Data Quality Engineer plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity and reliability of an organization’s data. By proactively identifying and resolving data quality issues, they contribute to the overall success of the data governance program and enable data-driven decision-making based on trustworthy information.

Data quality best practices - a step-by-step guide to improve data quality
- Learn the best practices in starting and scaling data quality
- Learn how to find and manage data quality issues
The Importance of Data Quality
Data quality is the cornerstone of effective data governance. It determines whether the data managed under governance policies and standards is truly usable and valuable for the business. Proving this value to business sponsors is essential for securing continued support and investment in data governance initiatives.
Measuring data quality is the most reliable way to verify the effectiveness of data governance standards and practices. It reveals how well data teams are adhering to these guidelines and the positive impact they have on the overall business value of data assets.
Organizations with global Data Governance bodies should track data quality and compare health scores across departments to identify which areas are excelling in data governance and which may need additional support. To ensure a fair and meaningful comparison, it is crucial to reuse the same definition of data quality health scores, such as data quality KPIs, and monitor them consistently across aligned data quality dimensions.
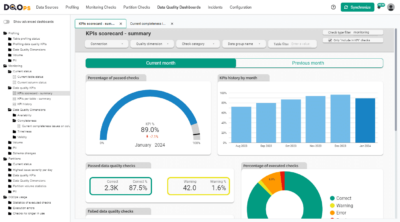
Data quality dashboards and global data quality scorecards are powerful tools for visualizing these metrics and comparing performance across business units. They offer a clear and concise overview of data quality health, enabling organizations to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, ultimately fostering a culture of data excellence.
What is the DQOps Data Quality Operations Center
DQOps is a data observability platform designed to monitor data and assess the data quality trust score with data quality KPIs. DQOps provides extensive support for configuring data quality checks, applying configuration by data quality policies, detecting anomalies, and managing the data quality incident workflow.
DQOps is designed to support both technical users, such as Data Engineers, and also to allow non-technical users, such as Business Data Stewards, to define and manage data quality checks and rules. The data quality dashboards provide a convenient way to measure data quality KPIs for each table or business area. The data quality dashboards can be customized to create specialized data quality scorecards that will track the process of implementing data governance policies and standards by measuring the data quality health scores across data domains.
You can set up DQOps locally or in your on-premises environment to learn how DQOps can monitor data sources and ensure data quality within a data platform. Follow the DQOps documentation, go through the DQOps getting started guide to learn how to set up DQOps locally, and try it.
You may also be interested in our free eBook, “A step-by-step guide to improve data quality.” The eBook documents our proven process for managing data quality issues and ensuring a high level of data quality over time. This is a great resource to learn about data quality.

Principles of Data Quality – Definition, Detection, Cleansing

What is Data Conformity? Definition, Examples, and Best Practices

What is Stale Data? Definition, Examples, and Best Practices

What are Data Governance Policies? Examples and Best Practices

What is Data Lineage? Meaning, Examples, Best Practices