A data steward is responsible for ensuring the quality, accuracy, and consistency of an organization’s data assets. They are the guardians of data integrity, playing a critical role in establishing and enforcing data governance policies and standards. Data stewards act as a bridge between business users and IT, possessing both a deep understanding of the business context and a solid grasp of technical data management principles.
Their primary focus is to ensure that data is fit for its intended purpose, adhering to defined quality metrics, and complies with relevant regulations. This involves activities like data profiling, metadata management, data lineage tracing, and implementing data quality rules and validation processes. Data stewards also play a key role in resolving data quality issues, identifying root causes, and driving improvements to data processes.
Table of Contents
The Need for Data Stewardship
In today’s world, data is quickly becoming the most valuable asset for many organizations. It’s the fuel that drives business processes, informs decision-making, and enables communication with customers and partners. However, the sheer volume and complexity of data is constantly growing. This means that datasets can quickly become outdated or even incorrect.
Organizations simply cannot afford to make decisions based on invalid or outdated data. Imagine sending a customer an invoice for a payment they’ve already made – it damages your credibility and can lead to serious customer dissatisfaction. In regulated industries, inaccurate data can also lead to compliance issues and hefty fines.
To avoid these pitfalls, organizations that prioritize effective data management are creating dedicated roles for overseeing the health of their data. These individuals are called data stewards. They are power users who understand both the intricacies of the business and the underlying structure of the data stored in databases. Their job is to ensure that the data remains accurate, relevant, and trustworthy.
Data Steward Role Definition
A data steward is a guardian of an organization’s data. Their primary responsibility is to ensure that data is accurate, complete, and used appropriately throughout the organization.
Key responsibilities and activities of a data steward include:
- Defining and enforcing data standards: Data stewards work with various teams to establish clear rules and guidelines for data creation, storage, and usage. They ensure everyone adheres to these standards, maintaining data consistency and quality.
- Monitoring and improving data quality: Data stewards actively track the health of data assets. They identify and resolve any data issues that arise, such as inconsistencies, inaccuracies, or missing information. They may also implement processes and tools to proactively prevent data quality problems.
- Managing metadata: Metadata, or data about data, is crucial for understanding the context and meaning of data. Data stewards oversee the creation, maintenance, and accuracy of metadata. This ensures that data is easily discoverable, understandable, and used correctly.
- Facilitating data access and sharing: Data stewards help establish and maintain processes for securely accessing and sharing data within the organization. They ensure that data is available to those who need it, while also protecting sensitive information.
- Collaborating with stakeholders: Data stewards work closely with various teams across the organization, including IT, business users, and data analysts. They act as a bridge between these groups, fostering communication and understanding around data.
- Staying up-to-date on data regulations: Data stewards keep abreast of any relevant data privacy regulations or industry standards. They ensure that the organization’s data practices comply with these requirements, mitigating legal and reputational risks.
Overall, data stewards play a critical role in ensuring that data is treated as a valuable asset within an organization. Their work enables informed decision-making, effective operations, and trustworthy insights.
Business and Technical Data Stewardship
In larger organizations, the role of a data steward may be further divided into two specialized functions: business data stewardship and technical data stewardship. This separation allows for greater focus and expertise in managing data across different domains.
Business data stewards are primarily concerned with the business context and meaning of data. They possess a deep understanding of the organization’s processes, goals, and data requirements. They act as the voice of the business, ensuring that data aligns with strategic objectives and supports decision-making. Their focus is on data governance, defining data standards, and communicating data quality expectations to stakeholders.
On the other hand, technical data stewards have a strong technical background and are responsible for the implementation and maintenance of data systems. They handle tasks such as data modeling, data integration, and data quality control. They are skilled in using tools and technologies to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and security. By separating these roles, organizations can leverage both business acumen and technical expertise to manage their data assets effectively.
The roles and responsibilities of these two types of data stewards are described in the infographic below.
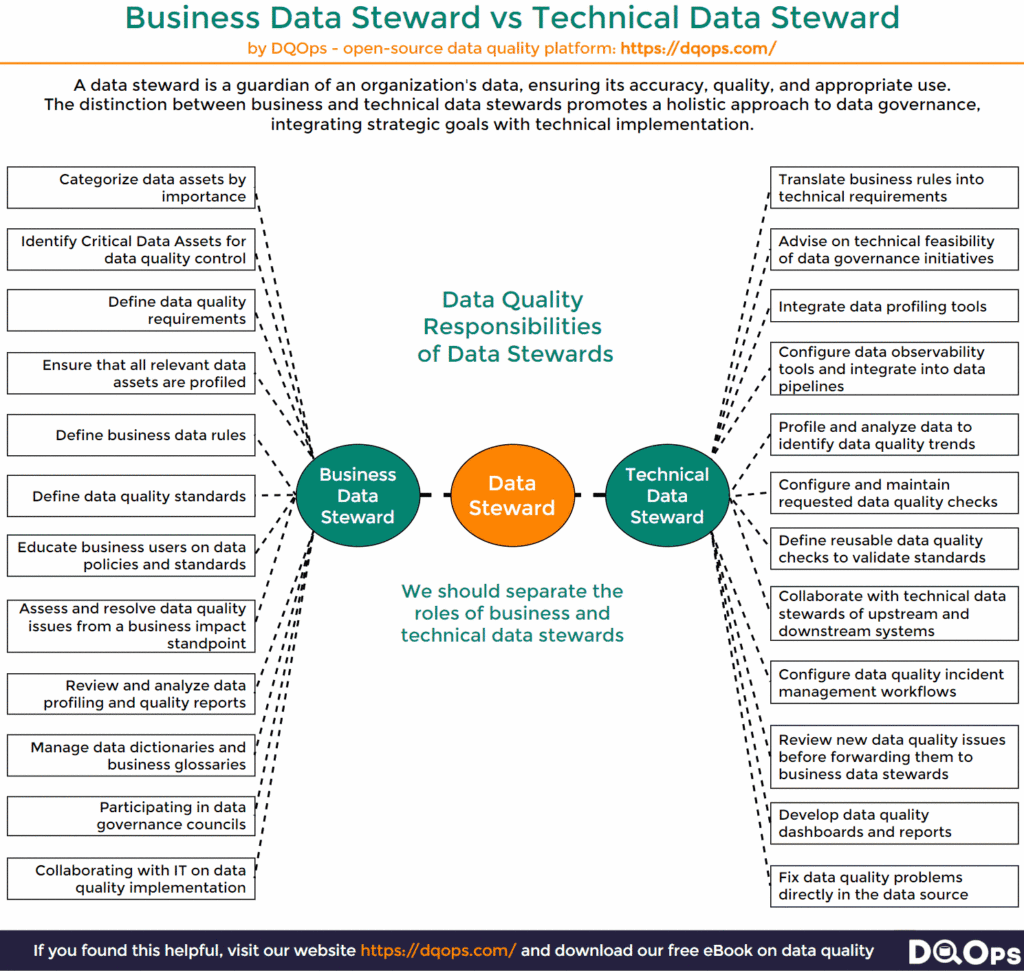
Business Data Steward Role and Responsibilities
As the bridge between business needs and data management, the Business Data Steward is vital in ensuring data is used effectively and strategically within the organization. Their key activities and responsibilities revolve around understanding and translating business requirements into actionable data practices.
- Data Governance Champion: The Business Data Steward actively participates in data governance initiatives, advocating for policies and procedures that support business goals and comply with regulations. They help establish and enforce data standards, ensuring consistency and quality across the organization.
- Data Quality Advocate: They monitor data quality from a business perspective, identifying and escalating potential issues that could impact decision-making or operations. They work with technical data stewards and other teams to resolve data quality problems and improve overall data health.
- Metadata Maestro: The Business Data Steward is responsible for defining and documenting business metadata, providing context and meaning to data elements. They ensure that metadata is accurate, up-to-date, and easily accessible to those who need it.
- Business Translator: They act as a liaison between business users and technical teams, translating business requirements into technical specifications. They also help educate business users on data policies, standards, and best practices, promoting data literacy across the organization.
- Data Access Gatekeeper: Business Data Stewards manage data access requests, ensuring that sensitive information is protected while still enabling appropriate data sharing and collaboration.
By fulfilling these responsibilities, Business Data Stewards empower the organization to make informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage through effective data utilization. They are the champions of data-driven insights, ensuring that data serves as a strategic asset rather than a liability.
Technical Data Steward Role and Responsibilities
The Technical Data Steward is the backbone of data quality and integrity within an organization. Their expertise lies in understanding the technical intricacies of data systems and ensuring that data is managed effectively from a technical standpoint.
- Data Quality Engineer: The Technical Data Steward implements data quality rules, performs data profiling and analysis to identify quality issues and trends. They proactively address data problems by cleansing, standardizing, and enriching data, ensuring its accuracy and reliability.
- Metadata Architect: They define and manage technical metadata, creating a comprehensive data dictionary that describes the structure, relationships, and lineage of data elements. They ensure that metadata is consistent, accessible, and aligned with business definitions.
- Data Integration Specialist: The Technical Data Steward plays a crucial role in integrating data from various sources, ensuring that data flows seamlessly across systems. They handle tasks such as data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL), ensuring data consistency and integrity during the integration process.
- Data Security Guardian: They implement and maintain data security measures, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access or breaches. They work closely with IT security teams to ensure that data is stored, transmitted, and accessed securely.
- Technical Advisor: The Technical Data Steward provides technical guidance to business data stewards and other stakeholders, helping them understand the technical implications of data management decisions. They collaborate on data governance initiatives, translating business requirements into technical solutions.
By fulfilling these responsibilities, Technical Data Stewards ensure that data is technically sound, reliable, and secure. They lay the foundation for effective data analysis, reporting, and decision-making, enabling the organization to harness the full potential of its data assets. Their work is crucial in maintaining data integrity, fostering trust in data-driven insights, and supporting the organization’s overall data strategy.
Tools for Effective Data Stewards
Data stewards, whether business-focused or technical, cannot perform their roles efficiently without the support of various tools that enable data governance practices. These tools streamline processes, enhance collaboration, and ensure the overall health of data assets.
- Data Catalog Platform: A data catalog platform acts as a central repository for documenting data sources, their definitions, and relationships. It allows data stewards to create a comprehensive inventory of data assets, facilitating data discovery, understanding, and governance.
- Data Quality Platform: A robust data quality platform is essential for validating the quality of data assets and managing data cleansing workflows to address any issues. This platform supports several crucial practices that are vital for ensuring data health:
- Data Profiling: Data profiling involves performing a data quality assessment to review the quality of a new data asset, such as a table. It calculates a baseline data quality score, helping data stewards understand if the data requires cleansing and how effective the cleansing efforts have been.
- Data Quality Management: This capability allows for defining custom data quality standards and running various types of data quality checks on monitored data sources. It helps proactively identify and address data quality issues.
- Data Observability: This feature enables continuous monitoring of data sources to detect anomalies and data quality issues without the need to pre-define data quality rules and configure their thresholds. This proactive approach allows for faster issue identification and resolution.
- Data Quality Incident Workflow Management: A data quality platform can send notifications when new data quality issues are detected and assign them to the appropriate data team for resolution. This streamlined workflow management ensures timely and effective issue remediation.
By leveraging these tools, data stewards can establish a robust data governance framework, ensuring data quality, accuracy, and compliance across the organization. These tools empower data stewards to fulfill their responsibilities effectively and contribute to the overall success of data-driven initiatives.

Data quality best practices - a step-by-step guide to improve data quality
- Learn the best practices in starting and scaling data quality
- Learn how to find and manage data quality issues
What is the DQOps Data Quality Operations Center
DQOps is a data observability platform designed to monitor data and assess the data quality trust score with data quality KPIs. DQOps provides extensive support for configuring data quality checks, applying configuration by data quality policies, detecting anomalies, and managing the data quality incident workflow.
DQOps is a unique data quality platform that combines traditional data quality processes with Data Observability. DQOps provides a code-first approach for technical data stewards and data engineers and a no-code user interface for less technical data stewards who prefer to perform data profiling using a web interface.
You can set up DQOps locally or in your on-premises environment to learn how DQOps can monitor data sources and ensure data quality within a data platform. Follow the DQOps documentation, go through the DQOps getting started guide to learn how to set up DQOps locally, and try it.
You may also be interested in our free eBook, “A step-by-step guide to improve data quality.” The eBook documents our proven process for managing data quality issues and ensuring a high level of data quality over time.