Last updated: July 22, 2025
How to Detect Invalid Dates? Examples and Best Practices
Read this guide to learn how to detect invalid dates in data, such as dates in the future or out of reasonable range and dates in a wrong format.
The data quality checks that detect invalid dates are configured in the datetime category in DQOps.
Types of invalid dates
The most common reasons why invalid dates enter into the data platform are:
-
A human error occurs when entering the date into an application manually.
A user made a small mistake, typing the wrong day or month. Many manual errors lead to entering dates in the future. -
The data pipeline was converting text values to dates, but the dates were written in an invalid format. For example, the transformation logic expected dates in the MM/DD/YYYY format, but dates were written in a reversed DD/MM/YYYY format.
-
The developers used a distant date in the future or in the past to identify special or missing dates. The most common special dates are 1900-01-01 and 2099-12-31.
Invalid dates in the dataset lead to wrong results in dashboards that are grouping values by date.
Dates in the future
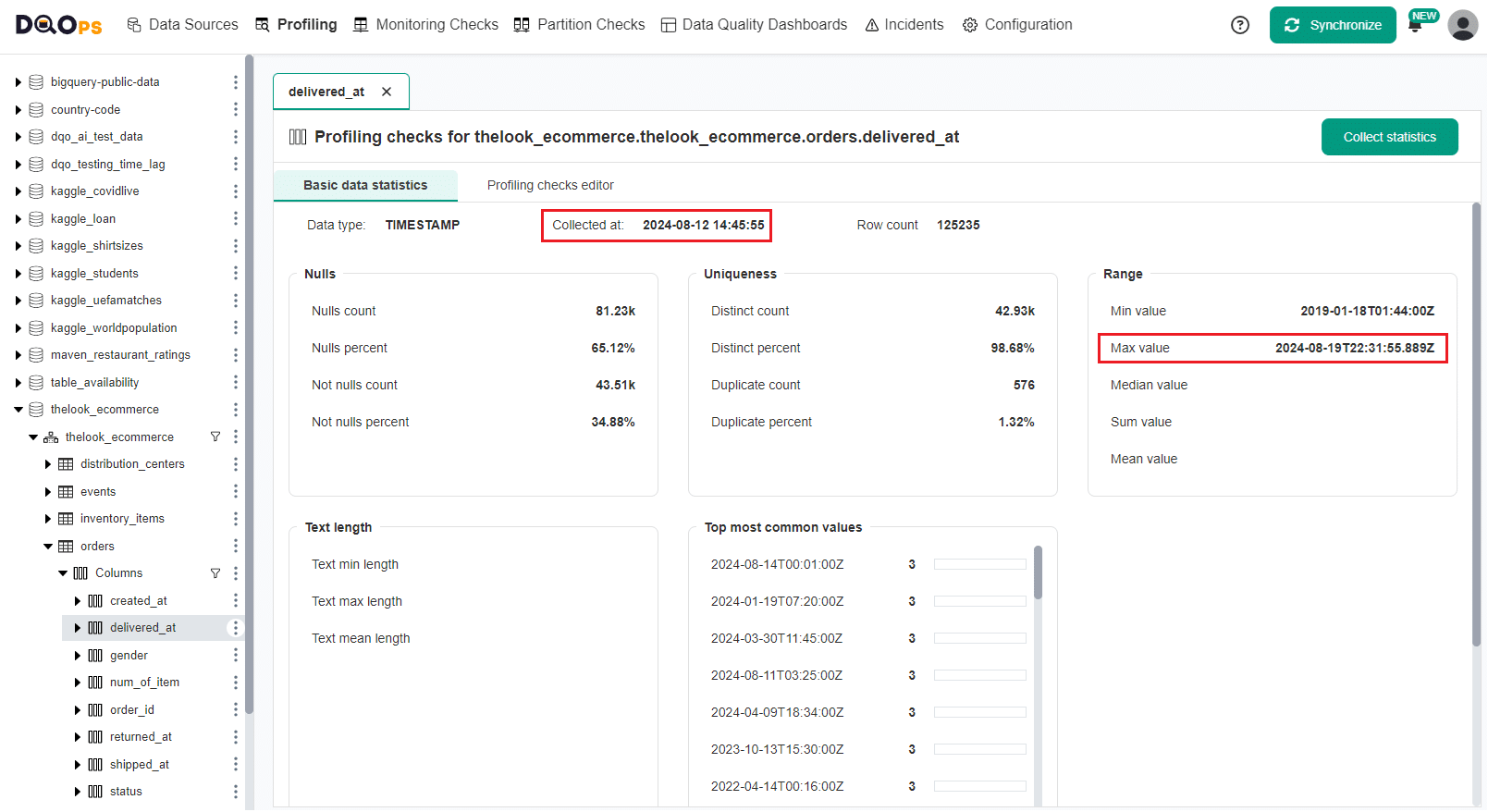
Future dates are caused mainly by manual data entry. The following example shows profiling results of a delivered_at column for an e-commerce platform. The most recent (maximum) date is after the current time when the table was profiled. It indicates that the delivery date is in the future.
Detecting future dates in UI
The date_values_in_future_percent data quality check finds dates in the future and measures the percentage of rows having future dates. The max_percent parameter controls the maximum accepted percentage of invalid rows.
Future dates error sampling in UI
To assist with identifying the root cause of errors and cleaning up the data, DQOps offers error sampling for this check. You can view representative examples of data that do not meet the specified data quality criteria by clicking on the Error sampling tab in the results section.
For additional information about error sampling, please refer to the Data Quality Error Sampling documentation.
Detecting future dates in YAML
The date_values_in_future_percent check is easy to enable. The following example shows the configuration as a daily monitoring check.
How to configure a tolerance time window
The date_values_in_future_percent check detects future dates, rejecting all dates even a few seconds after the current time. You can customize the date_values_in_future_percent check by creating a custom data quality check. It can use a different calculation formula that rejects dates at least seven days ahead of now.
An alternative method is to define a calculated column that subtracts a few days from the monitored column.
Dates out of range
The date_in_range_percent asserts that all date values are within a reasonable range. This check detects rows with corrupted or fake dates, such as 1900-01-01 or 2099-12-31.
Configure date in range check in UI
The date_in_range_percent check is configured with three parameters.
-
min_date parameter that is the earliest accepted date inclusive. The default value is 1900-01-02 to exclude a common placeholder date 1900-01-01.
-
max_date parameter that is the latest accepted date inclusive. The default value is 2099-12-30 to exclude a common placeholder date 2099-12-31.
-
min_percent parameter that is the minimum percentage of valid dates. The default value is 100%. DQOps measures only the percentage of not null date values. If only two rows store not null values and one value is out of range, the calculated percentage is 50% independent of the table size.
Configure date in range check in YAML
The date_in_range_percent check requires the configuration of the parameters described before.
Text column match date format
Text columns in the landing zone tables are often loaded as raw tables with only text columns. The data pipeline parses text values to a desired data type. Parsing integer or numeric values is simple, not generating confusion about the data format. But date values must match one of the popular formats. We cannot let the transformation engine detect the date format because the date detection logic cannot distinguish "01/02/2024" between February 1st, 2024, and January 2nd, 2024, leading to loading invalid dates. We can prevent these errors by asserting that all values match the same expected date format.
The following sample shows an extract from a text column that contains dates in mixed formats. The last row is different.
| Text column that should be a date |
|---|
| 2024-02-01 |
| 2024-02-02 |
| 2024-02-03 |
| 2024-02-04 |
| 02/05/2024 |
Asserting date formats in UI
We will use a sample column that contains dates in the ISO 8601 format. The profiling result shows some samples from the column.
The text_match_date_format_percent examines text columns (char, varchar, string, etc.), trying to match all column values to an expected date format. The parameters of the text_match_date_format_percent check are:
-
date_format parameter accepts one of the date formats supported by DQOps.
-
min_percent is the rule parameter to decide how many percent of non-null column values must match the expected format.
Asserting date formats in YAML
The configuration of the text_match_date_format_percent check uses a list of date formats supported by DQOps.
| Date format constant | Sample date |
|---|---|
MM/DD/YYYY |
12/31/2023 |
YYYY-MM-DD |
2023-12-31 |
DD/MM/YYYY |
31/12/2023 |
DD-MM-YYYY |
31-12-2024 |
DD.MM.YYYY |
31.12.2024 |
The configuration of the text_match_date_format_percent check in YAML is shown below.
List of datetime checks at a column level
| Data quality check name | Friendly name | Data quality dimension | Description | Standard check |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| date_values_in_future_percent | Maximum percentage of rows containing dates in future | Validity | Detects dates in the future in date, datetime and timestamp columns. Measures a percentage of dates in the future. Raises a data quality issue when too many future dates are found. | |
| date_in_range_percent | Minimum percentage of rows containing dates within an expected range | Validity | Verifies that the dates in date, datetime, or timestamp columns are within a reasonable range of dates. The default configuration detects fake dates such as 1900-01-01 and 2099-12-31. Measures the percentage of valid dates and raises a data quality issue when too many dates are found. | |
| text_match_date_format_percent | Minimum percentage of rows containing text values that match a date format | Validity | Verifies that the values in text columns match one of the predefined date formats, such as an ISO 8601 date. Measures the percentage of valid date strings and raises a data quality issue when too many invalid date strings are found. |
Reference and samples
The full list of all data quality checks in this category is located in the column/datetime reference. The reference section provides YAML code samples that are ready to copy-paste to the .dqotable.yaml files, the parameters reference, and samples of data source specific SQL queries generated by data quality sensors that are used by those checks.
What's next
- Learn how to run data quality checks filtering by a check category name
- Learn how to configure data quality checks and apply alerting rules
- Read the definition of data quality dimensions used by DQOps