Last updated: July 22, 2025
How to Detect Table Schema Changes? Examples and Best Practices
Read this guide to learn how to detect table schema changes, such as missing columns, missing tables, data type changes, or reordering the columns.
The table schema change detection checks are configured in the schema category in DQOps.
What is a schema change
The source tables can be modified in source systems for many reasons. A new version of the application is installed. A fact table is expanded to include new dimensions. Or, the previous column data type couldn't store some data. An unexpected table schema change affects data pipelines and can also affect downstream systems.
Types of schema changes
DQOps can detect the following types of table schema changes.
-
The count of columns in a table has changed. This change is caused by adding or removing a column, but monitoring the column count will not detect that a column was renamed, which does not change the column count.
-
A known column is missing.
-
A list of columns has changed. This type of check also detects that a column was renamed.
-
The list and order of columns has changed. This check detects that the columns were reordered. Column reordering happens when new Parquet or CSV files are built using a different transformation logic.
-
The column data types changed. DQOps can detect that the data type has changed; for example, an integer column was changed to a float column, or a varchar(50) column was extended to varchar(100) to fit longer values.
Schema checks in DQOps
DQOps uses two types of table schema detection checks.
-
Table-level schema checks are configured for a whole table. They identify any schema changes but cannot recognize a modified column.
-
Column-level schema checks are configured on a column that was known when importing the table metadata. DQOps can detect missing columns or column data type changes, identifying the changed column.
Table-level schema changes
DQOps supports the following schema change detection checks configured on a table level.
-
The column_count check counts the columns in the table and compares it to an expected number of columns
-
The column_count_changed check captures the count of columns in a table and compares it to the last known column count. It detects when the column count has changed.
-
The column_list_changed check detects when any column is added, removed, or renamed.
-
The column_list_or_order_changed check detects when any column is added, removed, or renamed. It also detects when the columns change their position in the table (columns are reordered).
-
The column_types_changed check detects when any column is added, removed, or renamed. Or when the data type, nullability status, or the column's length are changed.
Configuring table-level checks in UI
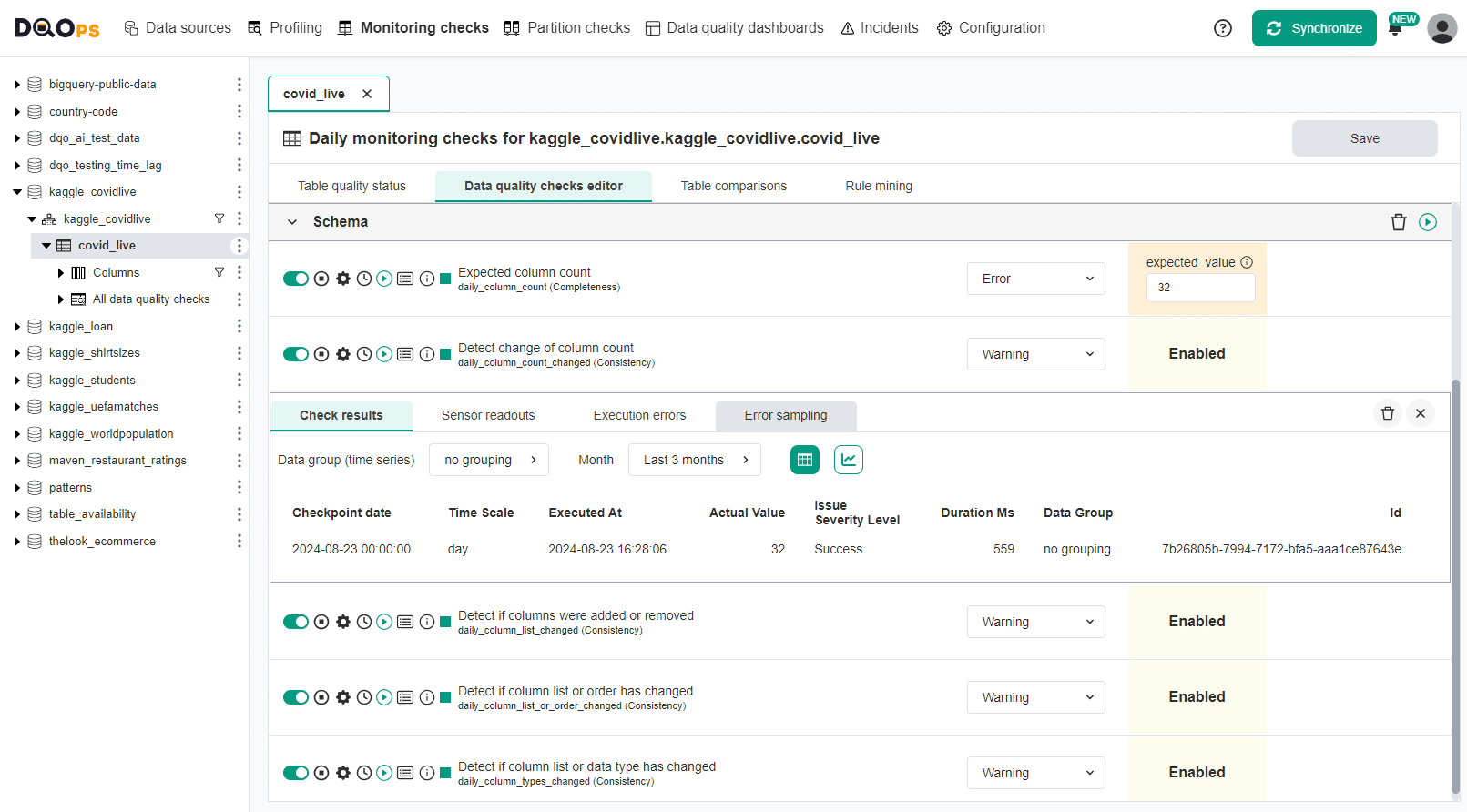
The only schema change detection check that has a parameter is the column_count check. It requires a value of the expected_value parameter, the desired column count.
The remaining schema change detection checks are configured by enabling the check at an expected data quality issue severity level. The change detection checks should be configured as daily monitoring checks to detect day-to-day changes.
Example of a schema change
In the meantime, a new column was added to the table using an SQL statement shown below.
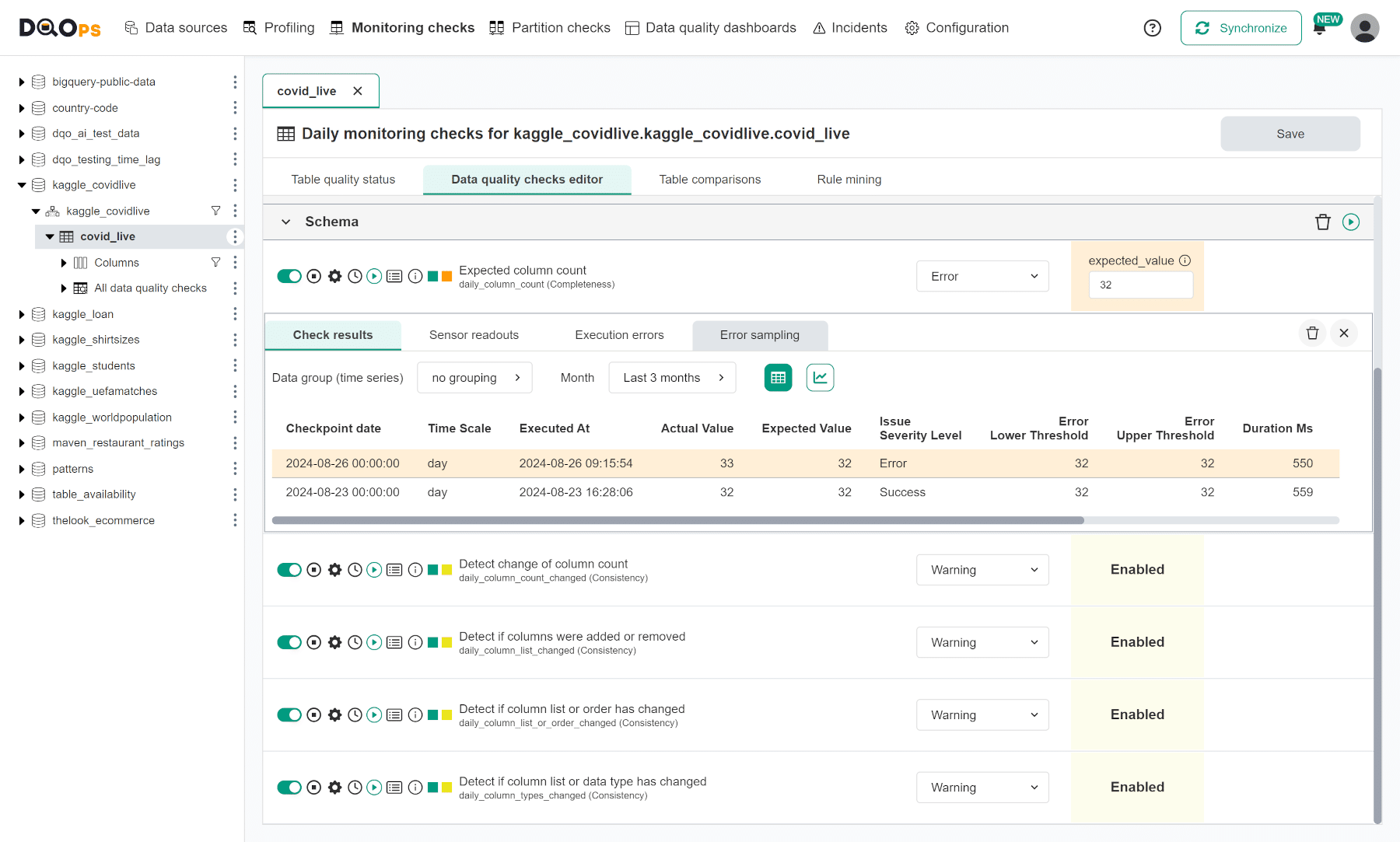
The following screenshot shows the data quality check editor on the next day.
DQOps detected new data quality issues for all types of schema changes because adding a new column is detected by all table-level checks. You can also review the example of detecting table schema changes, which shows how to detect other, more subtle changes to the table schema.
Configuring table-level checks in YAML
The configuration of table-level schema change detection checks in a DQOPs YAML file is shown below.
Column-level schema changes
DQOps supports the following schema change detection checks configured on a column level.
-
The column_exists check detects missing columns. It verifies that the column is still present in the table.
-
The column_type_changed check detects if the column data type, nullability status, or the column's length, precision, or scale has changed.
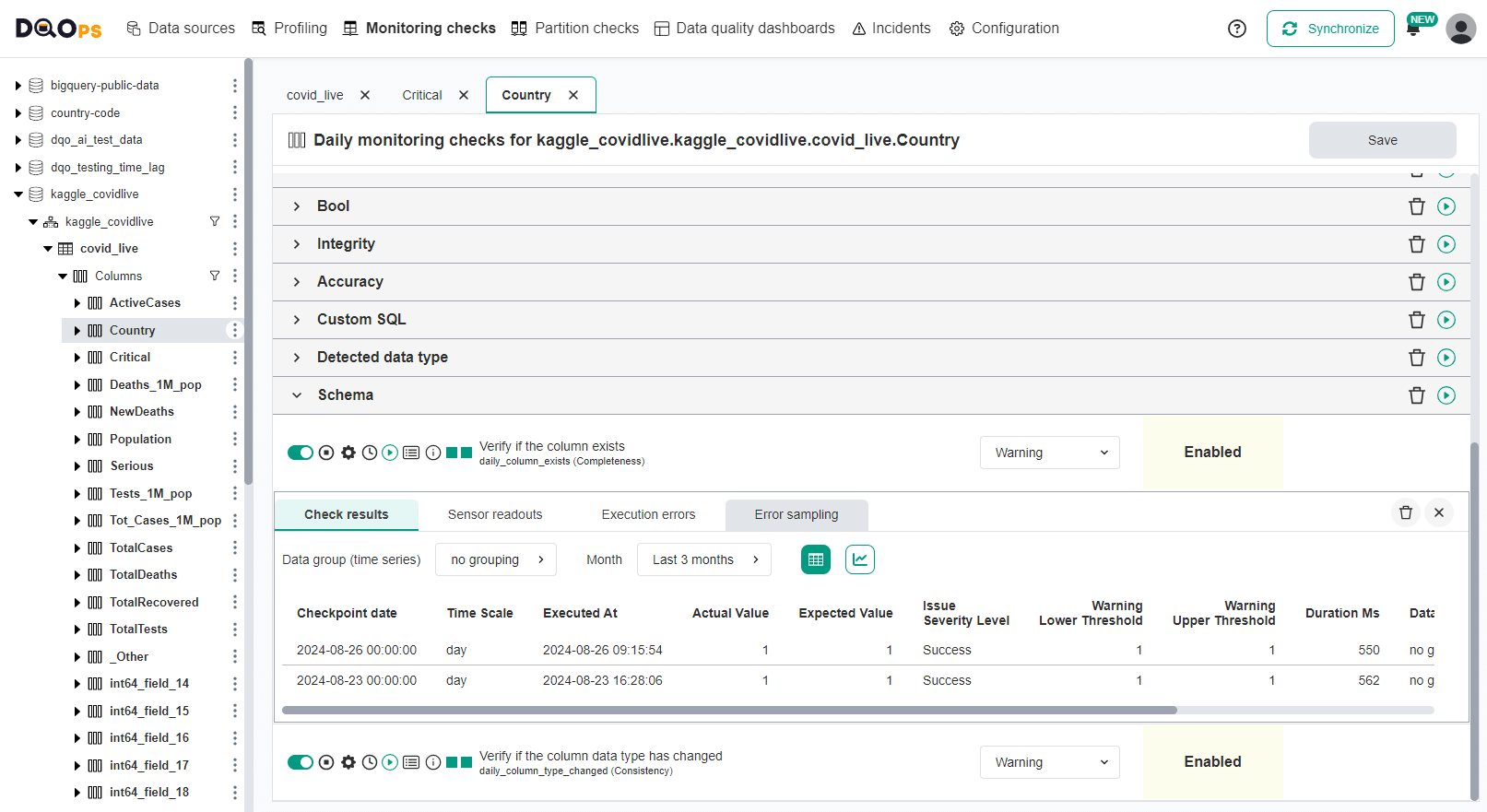
Configuring column-level checks in UI
The column-level schema change detection checks are configured using the data quality check editor on a column level.
Configuring column-level checks in YAML
The column's schema change detection checks are configured for each column.
Reviewing schema changes on dashboards
DQOps supports several data quality dashboards that are showing recent table schema changes.
Recent table schema changes
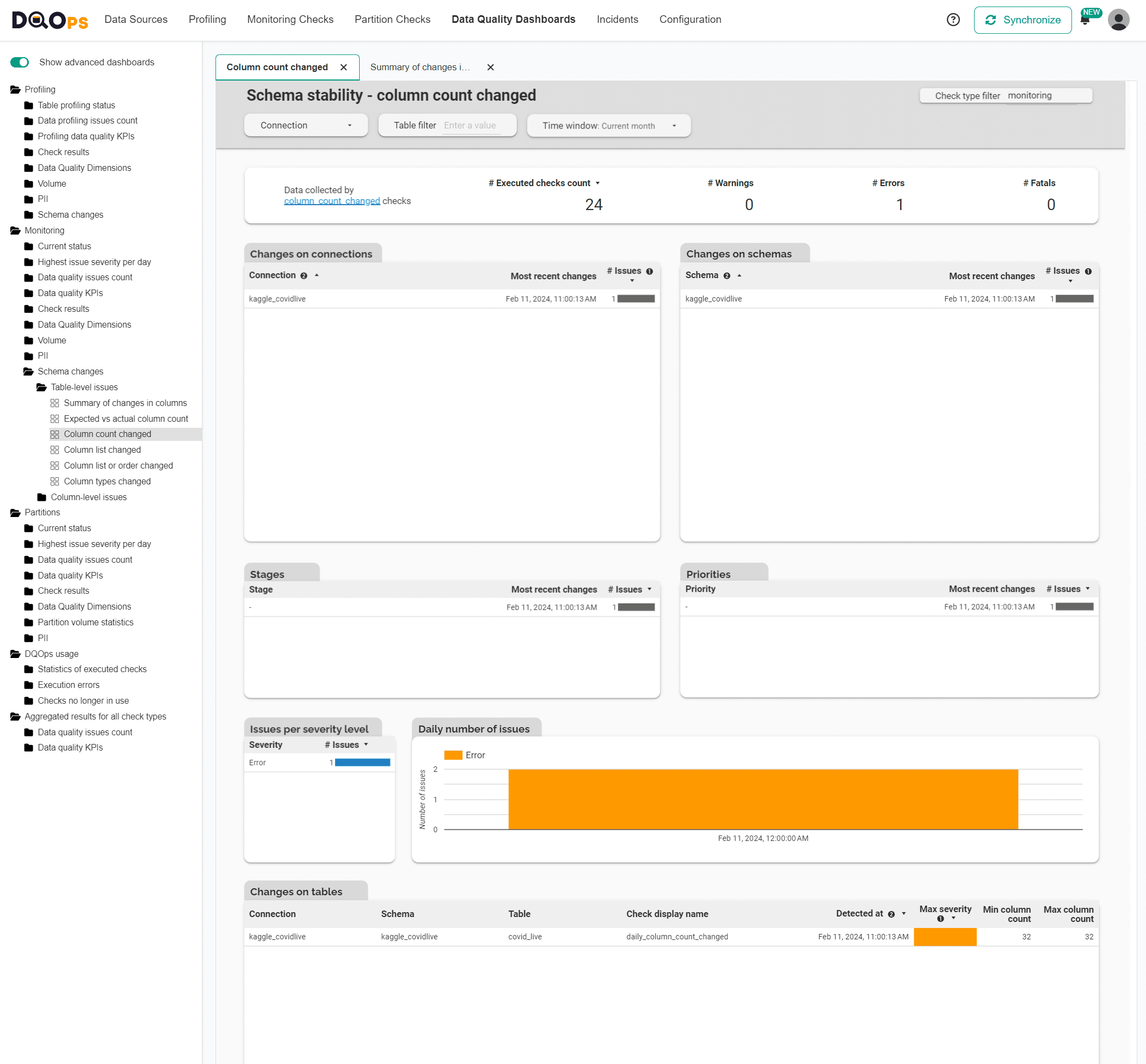
The summary dashboard shows all recent table schema changes of any type.
Detecting column count changes
The column count changes dashboard shows only the schema changes detected by the column_count_changed check. DQOps has similar data quality dashboards in the schema folder for different schema changes.
Use cases
| Name of the example | Description |
|---|---|
| Detect table schema changes | This example shows how to detect schema changes on the table using several schema change detection checks. |
List of schema checks at a table level
| Data quality check name | Friendly name | Data quality dimension | Description | Standard check |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| column_count | Expected column count | Completeness | A table-level check that retrieves the metadata of the monitored table from the data source, counts the number of columns and compares it to an expected number of columns. | |
| column_count_changed | Detect change of column count | Consistency | A table-level check that detects if the number of columns in the table has changed since the last time the check (checkpoint) was run. This check retrieves the metadata of the monitored table from the data source, counts the number of columns and compares it to the last known number of columns that was captured and is stored in the data quality check results database. | |
| column_list_changed | Detect if columns were added or removed | Consistency | A table-level check that detects if the list of columns has changed since the last time the check was run. This check will retrieve the metadata of a tested table and calculate a hash of the column names. The hash will not depend on the order of columns, only on the column names. A data quality issue will be detected if new columns were added or columns that existed during the previous test were dropped. | |
| column_list_or_order_changed | Detect if the column list or order has changed | Consistency | A table-level check that detects if the list of columns and the order of columns have changed since the last time the check was run. This check will retrieve the metadata of a tested table and calculate a hash of the column names. The hash will depend on the order of columns. A data quality issue will be detected if new columns were added, columns that existed during the previous test were dropped or the columns were reordered. | |
| column_types_changed | Detect if the column list or data type has changed | Consistency | A table-level check that detects if the column names or column types have changed since the last time the check was run. This check calculates a hash of the column names and all the components of the column's data type: the data type name, length, scale, precision and nullability. A data quality issue will be detected if the hash of the column data types has changed. This check does not depend on the order of columns, the columns can be reordered as long as all columns are still present and the data types match since the last time they were tested. |
Reference and samples
The full list of all data quality checks in this category is located in the table/schema reference. The reference section provides YAML code samples that are ready to copy-paste to the .dqotable.yaml files, the parameters reference, and samples of data source specific SQL queries generated by data quality sensors that are used by those checks.
List of schema checks at a column level
| Data quality check name | Friendly name | Data quality dimension | Description | Standard check |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| column_exists | Verify if the column exists | Completeness | A column-level check that reads the metadata of the monitored table and verifies if the column still exists in the data source. The data quality sensor returns a value of 1.0 when the column is found or 0.0 when the column is not found. | |
| column_type_changed | Verify if the column data type has changed | Consistency | A column-level check that detects if the data type of the column has changed since the last retrieval. This check calculates the hash of all the components of the column's data type: the data type name, length, scale, precision and nullability. A data quality issue will be detected if the hash of the column's data types has changed. |
Reference and samples
The full list of all data quality checks in this category is located in the column/schema reference. The reference section provides YAML code samples that are ready to copy-paste to the .dqotable.yaml files, the parameters reference, and samples of data source specific SQL queries generated by data quality sensors that are used by those checks.
What's next
- Learn how to run data quality checks filtering by a check category name
- Learn how to configure data quality checks and apply alerting rules
- Read the definition of data quality dimensions used by DQOps