Last updated: July 22, 2025
How to Detect Whitespace and NULL Value Placeholders? Examples
Read this guide to learn how to detect whitespaces, such as spaces, tabs, or special texts equivalent to a null value in text columns using SQL checks.
The data quality checks for detecting whitespace and empty value placeholders are configured in the whitespace category in DQOps.
Types of whitespaces
We can identify three types of blank texts that should be stored as NULL values.
What is an empty text
An empty text is stored in the column as zero-length string .
Some database engines allow the storage of both a NULL value or an empty string .
Empty strings cause issues in SQL queries because an empty string is not equal to a null value.
An SQL query WHERE column_name IS NULL will not find rows with empty values.
DQOps detects empty values using the following SQL condition.
What is a whitespace
A whitespace is a character that represents vertical space.
The whitespace characters are a space ' ' character and a tab '\t' character.
Whitespaces are detected in SQL by using a TRIM function.
DQOps uses the following SQL condition to detect that a column contains only whitespace instead of being empty or null.
What is a null placeholder
Various programming languages use a different name for a special object that identifies a missing value.
For example, Python uses None, and JavaScript uses undefined.
When the data pipeline converts these objects to a string, they may be written as texts None or undefined.
It happens when the data pipeline does not handle empty values correctly.
The following table shows the list of all common null placeholders.
| Null placeholder | Null placeholder | Null placeholder | Null placeholder |
|---|---|---|---|
null |
undefined |
missing |
nan |
none |
na |
n/a |
empty |
#n/d |
blank |
"" |
'' |
- |
'' (empty text) |
DQOps detects null placeholders using the following SQL condition.
WHERE column_name IN ('null', 'undefined', 'missing', 'nan', 'none', 'na', 'n/a', 'empty', '#n/d', 'blank', '""', '\'\'', '-', '')
Blank values data quality checks
DQOps has two types of data quality checks to detect blank values.
-
*_founddata quality checks that raise an issue when DQOps finds any blank value -
*_percentdata quality checks that measure the percentage of blank values
Detect any blank values
Enable the _found data quality checks to find blank values or accept a limited number of blank values.
Configure checks in UI
The blank detection checks are standard data quality checks in the "whitespace" category.
Configure checks in YAML
The blank detection checks are configured in the YAML file inside the whitespace node.
Measure the percentage of blank values
The measurement of blank percentages involves advanced checks that may not be visible in the user interface.
Configure checks in UI
To display non-standard checks, select the Show advanced checks checkbox. This will show the percentage of whitespace checks.
Configure checks in YAML
The percentage checks are easy to configure in a YAML file. The parameter max_percent controls the maximum accepted percentage.
Text surrounded by whitespace
DQOps has dedicated data quality checks to detect text values surrounded by whitespace characters such as space or tab. Additional whitespace can appear when the data is entered manually and the user accidentally adds extra space.
There is another problem with the data that is stored in legacy databases. Old databases used fixed-width character data types, such as CHAR(10). Text values stored in these old databases were filled with extra spaces to fill the remaining character positions. Text values extracted from these databases will contain additional space characters at the end of shorter texts.
The following table shows an example of a data quality issue related to the inconsistent presence of space characters around a text value.
| state_id | state_name | Whitespace before | Whitespace after |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | null | ||
| 2 | 'California' |
||
| 3 | ' Arizona' |
||
| 4 | 'Colorado ' |
||
| 5 | ' Florida ' |
Additional whitespace around values causes the following issues.
-
Two values that differ by extra whitespace around the text are not equal, leading to data duplication.
-
SQL queries using a GROUP BY clause will return additional rows.
-
SQL queries using joins will return no records when the columns that are joined differ by extra whitespace.
-
The database will need additional space to store the values.
DQOps supports two very similar checks that detect texts surrounded by whitespace.
-
The text_surrounded_by_whitespace_found check finds and counts texts surrounded by whitespace characters.
-
The text_surrounded_by_whitespace_percent check finds and measures the percentage of texts surrounded by whitespace characters.
Detecting text surrounded by whitespace in UI
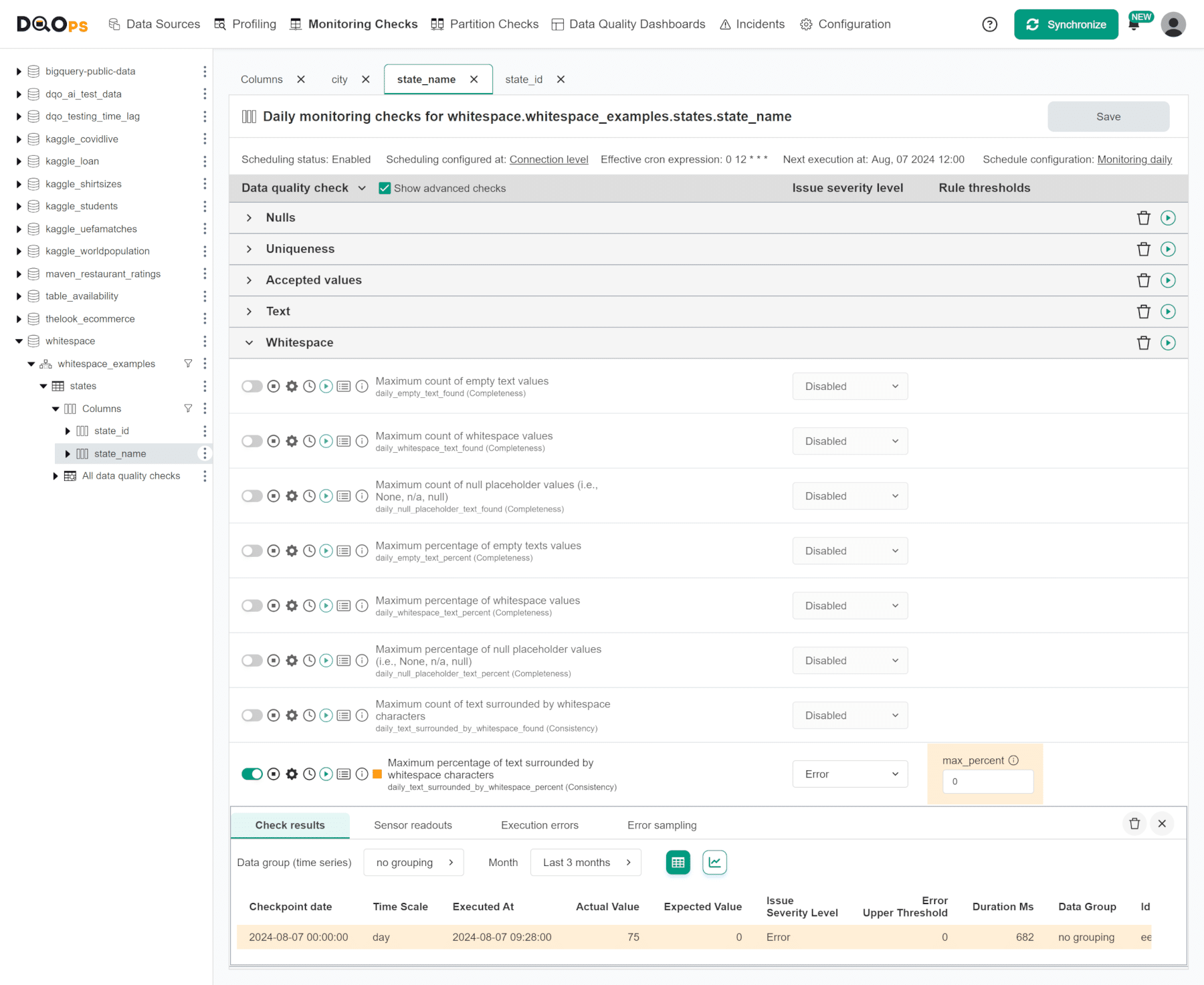
The text_surrounded_by_whitespace_percent check takes one parameter, the max_percent. When the default value 0% is used, DQOps will raise a data quality issue when any value surrounded by whitespace is found.
Please note that the DQOps data quality check editor shows this check after clicking the Show advanced checks checkbox.
The results in DQOps show that 75% of non-null values (three out of four) contained whitespace characters around the text.
Text surrounded by whitespace error sampling in UI
To assist with identifying the root cause of errors and cleaning up the data, DQOps offers error sampling for this check. You can view representative examples of data that do not meet the specified data quality criteria by clicking on the Error sampling tab in the results section.
For additional information about error sampling, please refer to the Data Quality Error Sampling documentation.
Detecting text surrounded by whitespace in YAML
The configuration of the text_surrounded_by_whitespace_percent check is straightforward.
List of whitespace checks at a column level
| Data quality check name | Friendly name | Data quality dimension | Description | Standard check |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| empty_text_found | Maximum count of empty text values | Completeness | This check detects empty texts that are not null. Empty texts have a length of zero. The database treats them as values different than nulls, and some databases allow the storage of both null and empty values. This check counts empty texts and raises a data quality issue when the number of empty values exceeds a max_count parameter value. | |
| whitespace_text_found | Maximum count of whitespace values | Completeness | This check detects empty texts containing only spaces and other whitespace characters. This check counts whitespace-only texts and raises a data quality issue when their count exceeds a max_count parameter value. | |
| null_placeholder_text_found | Maximum count of null placeholder values (i.e., None, n/a, null) | Completeness | This check detects text values that are well-known equivalents (placeholders) of a null value, such as null, None, n/a. This check counts null placeholder values and raises a data quality issue when their count exceeds a max_count parameter value. | |
| empty_text_percent | Maximum percentage of empty texts values | Completeness | This check detects empty texts that are not null. Empty texts have a length of zero. This check measures the percentage of empty texts and raises a data quality issue when the rate of empty values exceeds a max_percent parameter value. | |
| whitespace_text_percent | Maximum percentage of whitespace values | Completeness | This check detects empty texts containing only spaces and other whitespace characters. This check measures the percentage of whitespace-only texts and raises a data quality issue when their rate exceeds a max_percent parameter value. | |
| null_placeholder_text_percent | Maximum percentage of null placeholder values (i.e., None, n/a, null) | Completeness | This check detects text values that are well-known equivalents (placeholders) of a null value, such as null, None, n/a. This check measures the percentage of null placeholder values and raises a data quality issue when their rate exceeds a max_percent parameter value. | |
| text_surrounded_by_whitespace_found | Maximum count of text surrounded by whitespace characters | Consistency | This check detects text values that contain additional whitespace characters before or after the text. This check counts text values surrounded by whitespace characters (on any side) and raises a data quality issue when their count exceeds a max_count parameter value. Whitespace-surrounded texts should be trimmed before loading to another table. | |
| text_surrounded_by_whitespace_percent | Maximum percentage of text surrounded by whitespace characters | Consistency | This check detects text values that contain additional whitespace characters before or after the text. This check measures the percentage of text value surrounded by whitespace characters (on any side) and raises a data quality issue when their rate exceeds a max_percent parameter value. |
Reference and samples
The full list of all data quality checks in this category is located in the column/whitespace reference. The reference section provides YAML code samples that are ready to copy-paste to the .dqotable.yaml files, the parameters reference, and samples of data source specific SQL queries generated by data quality sensors that are used by those checks.
FAQ
The questions and answers for popular questions related to detecting whitespace characters.
What is a whitespace character
A whitespace character is any character that represents a blank space, such as a regular space, a tab, or a new line. These characters are often invisible to the human eye but can affect how data is processed and interpreted by databases. When users are previewing column values, the columns that contain values ending with whitespace look the same as trimmed values. However, the values don't match, and a query that uses a filter in the WHERE clause in SQL will not find all rows.
What is the valid name, "whitespace" or "white space"
Both "whitespace" and "white space" are used, but "whitespace" is generally considered the more technically correct and contemporary term, especially in computing and data management contexts. You'll find it used more frequently in technical documentation and programming.
How to check if a column value has space in SQL
To check for spaces in a SQL column, use the LIKE operator (e.g., column_name LIKE '% %') or remove spaces with TRIM and compare the result to the original column
(e.g., WHERE TRIM(column_name) <> column_name).
Remember that spaces are just one type of whitespace. For a thorough check, consider your database's specific functions or regular expressions.
How to check if a column value has space in SQL Server
In SQL Server, you can use all generic methods of detecting whitespace characters mentioned in the previous answer.
SQL Server also offers specialized functions like CHARINDEX to locate the position of a space within a string, giving you more precise control.
The following query will find a space character using TransactSQL in SQL Server:
What is the difference between using IS NULL or finding a whitespace in SQL?
IS NULL checks if a column value is explicitly defined as NULL, meaning it has no value at all. This is a specific state recognized by the database.
On the other hand, finding a whitespace (using LIKE, TRIM, etc.) means looking for characters like spaces, tabs, or newlines that represent "blank" space.
These are actual characters stored in the database, even though they might appear invisible.
Here's why this difference matters:
-
Database Storage: Some databases, notably Oracle, have a unique behavior. They might not store truly empty string values. Instead, they represent them as NULL values. This can lead to unexpected results if you're searching for empty strings but the database treats them as NULLs.
-
Configuration: Both Oracle and SQL Server allow you to configure how the database handles comparisons between empty strings and NULL values. This setting can affect query results and indexing. For instance, in Oracle, you can use the
ANSI_NULLSsetting to control this behavior. In SQL Server, this is influenced by theSET ANSI_NULLSoption. -
Sorting and Indexing: Empty strings and NULL values are treated differently in sorting operations and index construction. This can impact the performance and organization of your data.
How PostgreSQL handles NULL or empty value in GROUP BY?
PostgreSQL has a clear and consistent way of handling NULL and empty values in GROUP BY:
-
NULL values are grouped together: If a column has multiple NULL values, they will be treated as a single group in the
GROUP BYresult. -
Empty strings are grouped together: Similar to NULLs, all empty strings (
'') are considered the same and grouped into a single group. -
NULL and empty strings are distinct: Importantly, PostgreSQL distinguishes between NULL and empty strings. They are treated as separate groups in the
GROUP BYclause.
How to represent a tab character in SQL?
To represent a tab character in SQL, use CHAR(9) function. The ASCII code for a tab character is 9.
Some databases may allow you to directly insert a tab character using the Tab key or an escape sequence like \t, but CHAR(9) is the most reliable method in databases
that support this function.
Here are the examples of using the CHAR or similar functions in the most popular databases:
- SQL Server:
CHAR()is a standard function. - Oracle: Oracle uses
CHR()to achieve the same result. - PostgreSQL:
CHAR()is fully supported. - MySQL:
CHAR()is a standard function. - IBM DB2:
CHAR()is part of the standard SQL functions. - SQLite:
CHAR()is available.
How to remove whitespaces around a text in SQL?
To remove whitespaces around text in SQL, you can use the TRIM() function. It removes leading and trailing whitespace characters (spaces, tabs, newlines, etc.) from a string.
Here's a simple example:
This will return:
How to remove all spaces inside a text using SQL?
While TRIM() function removes spaces around text, to remove all spaces within the text, you'll need a different approach. Most databases offer a function like REPLACE().
This function replaces all occurrences of a specified character with another character. In this case, you'd replace all spaces (' ') with an empty string ('').
Here's how it works:
This will return:
What's next
- Learn how to run data quality checks filtering by a check category name
- Learn how to configure data quality checks and apply alerting rules
- Read the definition of data quality dimensions used by DQOps